202406151539
Status:
Background
4-2-1 formula of Holliday and Segar
Hypotonic maintenance solution
- originally suggested based on calculation
- periop use → hypoNa → permanent brain damage / death
- ∵ ↑ADH from stress & volume depletion
- risk of hyponatremic encephalopathy high for prepubescent children
- ∵ ↑ brain-size-to-cranial-vault ratio
- ↓ Na-K ATPase activity
- ↑ADH level in response to stress
- risk of hyponatremic encephalopathy high for prepubescent children
Dextrose
- traditionally 5% glucose added to paed maintenance infusion
- → hyperglycaemia in periop context
- ∵ surgical stress
- ↑ counter insulin hormone levels
- e.g. cortisol, glucagon, epinephrine, GH
- ↓ insulin
- ↑ counter insulin hormone levels
- → hyperglycaemia induced catabolic state
- ∵ surgical stress
- → hyperglycaemia in periop context
- Population high risk of hypoglycaemia
- infants
- liver disease
- malnourishment
- burns
- prolonged fasting
- glucose concentration of 1 - 2.5% adequate to prevent lipolysis & hypoglycaemia w/o risk of hyperglycaemia
| Risk factors for perioperative hypoglycaemia | |
|---|---|
| Patient-related risk factors | Age <12 months |
| Weight for age <5th percentile | |
| Failure to thrive | |
| ASA status ≥ III | |
| Metabolic disease | |
| Developmental delay | |
| Gastric or jejunal feeding tube | |
| Low glycogen reserve (parenteral nutrition, liver disease, beta blockers, diabetic mother) | |
| External risk factors | Malnutrition |
| Long fasting times | |
| Abdominal surgery |
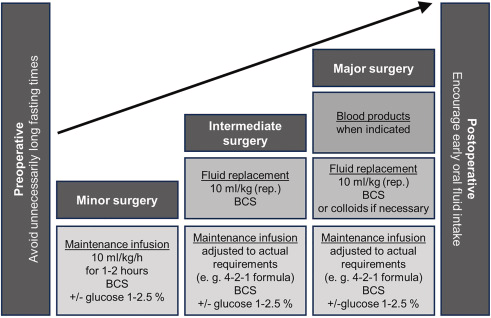
Maintenance infusion rate
- starting w/ 10ml/kg/h
- account for deficits from fasting
- assure stable homeostasis
- after 1-2h → adjust to actual requirements
- e.g. 4-2-1 formula
moderate certainty evidence from Cochrane that in children >6mo maintenance rate of 30ml/kg/h ↓ PONV in ASA 1 to 2 for ambulatory or short LOS procedures
Electrolyte requirement
- Na 3mmol/kg/day
- K 2mmol/kg/day
- Ca 0.3mmol/kg/day (normal) to 1mmol/kg/day (deficiency state)
Basal glucose requirement
- infants & children: 3-5mg/kg/min
- adults: 2-3mg/kg/min
D10 for hypoglycaemia: 2.5-5ml/kg over 3-5min
Fluid type
- isosmotic / isotonic
- effective osmolality similar to plasma (288mOsm/kgH2O)
- isoionic
- fluid contain physiological values of important plasma electrolytes
- isohydric = balanced
- potential BE of 0±10mmol/l
extracellular space larger in small children relative to BW, proportion of blood volume in the ECF is lower than in older children & adults (newborns 10%, infants 20%, adults 25%)
neonates
- limited physiological range for urine osm
- preterm: 50 - 600mOsm/L
- term infants: 50 - 800mOsm/L
- (adults 40-1200mOsm/L)
- → limited capacity to excrete / conserve Na
- ↑rate of glucose utilisation ∵ metabolic demands of developing brain
- 4-8mg/kg/min glucose
- 10ml/kg/h of glucose 1%, 2% & 4% in LR equivalent in newborns
- 2-4% dextrose fluids more effective at preventing untoward events